Broken Links: An SEO Guide to Finding and Fixing 404 Errors

In the highly competitive digital world, the success of your website hinges on numerous factors, one of them being the functionality of your links.
Broken links are a common, yet often overlooked, technical SEO issue that can significantly impact your site's quality, rankings, and overall user experience.
This article will serve as a comprehensive, step-by-step guide on how we at GR0 find and fix broken links on our client’s websites. We hope this guide will help demystify this facet of technical SEO and help you improve both your site's performance and your user's experience.
What Are Broken Links?
Broken links, also known as dead links, are links that lead to pages that do not exist. When a user or search engine bot tries to follow a broken link, they will usually encounter a “404 Error Page.” This error is among several HTTP status codes in the 400 or 4xx range, indicating broken or missing content and by far the most common.
The causes of broken links are diverse. They can occur when linked content is moved or deleted, causing what is known as link rot. A study by Harvard Law School of over 2 million hyperlinks showed that as time goes on, link rot on the web increases exponentially, with links from 10 years ago becoming broken at a 43% rate!

Source: https://www.cjr.org/analysis/linkrot-content-drift-new-york-times.php
Changes to the site's URL structure during a site migration, misspelled URLs, or page and content deletions can also cause broken links.
Why Is It Important To Fix Broken Links?
Broken links, be they internal links that lead to other pages on your site or external links directing to other websites, are detrimental in many ways.
Firstly, they disrupt the user experience. Clicking on a link only to be met with an error page is frustrating for users and may discourage them from further exploring your site. Any time a user doesn't get what they thought they would when they click a link on your site it encourages them to leave.
From an SEO perspective, broken links are harmful because search engines, like Google, consider them while determining the quality of your site. When a search engine's crawler, also known as a spider, encounters a large amount of broken links, it can signify poor maintenance. If too many of these are present it can lead to reduced crawling and potentially Google seeing your site as “low-quality.”
In the realm of digital marketing, trust is a valuable currency. Frequent encounters with broken links can erode your audience's trust, negatively affecting your brand reputation. While fixing broken links is often the most effective way to preserve your site’s quality, having a functional and attractive 404 landing page is an absolute must for preserving brand image and user experience. A 404 landing page can greet users and help them get back to useful content even if you’re unaware a broken link exists!
How To Check for Broken Internal Links
Knowing how to find broken pages and links is an all-important first step in beginning to fix the quality of your website. There are a handful of tools and methods SEOs use. We’ll cover below the ones we at GR0 use, and a few alternatives we think might be useful.
1. Use a Web Crawler
No SEO’s tool kit is complete without a proper web crawler. Website crawling tools or SEO spiders are designed to mimic how search engines crawl websites, thereby helping to uncover all sorts of SEO issues, including broken links. Using a web crawling tool is our first step in discovering where broken pages exist on sites as well as where those broken pages are linked to.
Selecting a Crawling Tool
There is no shortage of web crawlers available, both in paid and free versions. Some popular ones are Screaming Frog SEO Spider, SiteBulb, Botify, Jet Octopus, as well as the audit tools within larger tool suites like Ahrefs and SEMRush.
All these tools have their unique features and advantages, but they all perform the essential function of detecting broken links effectively. Here at GR0, we’re partial to Screaming Frog due to its versatility and ability to handle small, medium, and large sites fairly well. The free version even lets you crawl up to 500 pages which is great for small sites and those new to SEO!
Configuring Crawling Settings
After selecting your preferred tool, you'll need to configure it to suit your requirements. You can set up the crawler to scan all the pages or specific sections of your site. This is great if you have a larger site and you only want to focus on a particular portion. It must be noted, however, that to get the clearest picture of all the broken links across your site, crawling the entire site is the only way to go.
It's a good practice to ensure your SEO spider is set to follow both internal and external links though the fixes for these will be very different, If your site is heavily coded in JavaScript, you may need to make sure that rendering is turned on so it can find any links that only appear after a page is rendered.
We also suggest making sure your XML Sitemap is part of the crawl, as it functions as your list of all your pages you want search engines to see.

Analyzing Crawl Results for Broken Links
Once the crawl is complete, the tool will provide you with a report detailing all the information about your site's health, including broken pages. You can usually find these under “Response Codes” or “HTTP Status” and look for 4xx errors, these can also be sorted by internal or external pages. In Screaming Frog, you need to select a broken page and then select the “inlinks” tab at the bottom to see all the places your site links to this broken page.

These tools often allow you to export data into Google Sheets, CSV, or Excel formats, we recommend exporting the inlinks to your broken pages so you sort and prioritize your issues. Obviously, the more links leading to a broken page, the bigger the issue, so use this to help maximize your efforts.
Something we always suggest, too, is manually checking your pages to be certain they’re actually broken and the links still exist. While things like AI and automated tools are great and can save tons of time, they’re not perfect.
2. Manual Checks
While this method isn’t suitable for sites with more than a handful of pages, we always encourage checking the status and links on a representative sample or key pages manually. Prioritize your most important pages, like the home page, social media links, and blog posts. Simply visit the page containing broken links and click them.
Using the data from your crawling tool, you can even narrow down the anchor text and surrounding content to make sure you’re following the problem links.
If you do encounter a link that says it's broken but actually works, it’s alright to move along and skip that. User experience is the key reason for fixing broken links, so if that is satisfactory, you’re usually in good shape. If large amounts of your broken links end up working, it might be time to ask for help (like reaching out to the professionals here at GR0), as you may have a deeper issue causing your site to appear broken.
Identifying Broken Links With Browser Extensions
You can also use browser extensions to check links. Extensions like the Ahrefs Toolbar (our favorite) and “Check My Links” for Chrome are free tools that scan web pages for broken links, highlighting them for easy identification. WordPress users can benefit from plugins like “Broken Link Checker,” which monitor and detect broken links.
This manual process can be tiresome and time-consuming, especially for larger websites. This is why we recommend starting with tools like website crawlers, like Screaming Frog, SEO browser extensions, and Google Search Console can be quite useful.
3. Using Google Search Console
As one of the most effective and free tools at your disposal, Google Search Console (GSC) should be among the first ports of call in your SEO journey. GSC is a site owner and SEO’s clearest look into how our sites perform and how Google sees and crawls a website. It helps monitor, troubleshoot, and improve your site's presence in Google Search results, broken links included.
How To Use Google Search Console
To begin using Google Search Console, you'll need to add and verify your ownership. Once your site is verified, navigate to the “Pages” report in the “Indexing” section. This report shows you any issues that Google's crawlers have found when indexing your website, including your broken pages.
The biggest section of this report is the “Why Pages Aren’t Indexed” section which is a massively useful tool for all aspects of your website's health.

Here, you'll find a list of URLs that Google couldn't find on your site, which usually means they're broken. Since Google crawls the entire web more than anyone, it can turn up broken pages an SEO crawler may not find.
Monitoring and Resolving Broken Links
Google Search Console is a great additional tool to check for broken pages you might have missed, as well as to see what Google thinks about the broken pages on your site. You can even use Google’s URL inspector on these pages to sometimes see the exact page Google found a broken link to your pages on. While it won’t give you every place you can find a potential broken link, it can help start your journey.
Keep in mind, Google Search Console updates its data every few days. Check the “last crawled” date next to your results to know when Google last identified this URL as broken. Google even gives you a button to validate your fixes once you’re done. Don't panic if the broken link still appears after you've fixed it and started validation. This process can take weeks or even months, depending on the size of your site.
How To Fix Broken Internal and External Links
Once you have identified the broken pages, the next step is implementing fixes. In this context, There are 3 key methods to fix broken internal links: removing the broken link, changing the broken link to a working URL and setting redirects on the broken pages.
Creating 301 Redirects for Internal Links
The 301 redirect is the most commonly used method to fix broken links. When you apply a 301 redirect to a broken URL, you're telling search engines that the page has permanently moved to a new location. According to Google both permanent (301) and temporary (302) redirects help to preserve rankings and pass link equity associated with the old URL. Google recommends you keep 301 redirects in place for at least a year to ensure all equity passes from the old page to the new. Evidence also suggests that over time Google will treat a temporary 302 redirect like its permanent so if you forget or see a 302 instead of a 301 it isn't a cause for great concern. Google's John Mueller lays out on twitter how this might happen:

If you’re working within a CMS like WordPress, Wix, or Shopify, they will have methods within their system and rules that will allow you to designate what pages need to receive these redirects. If you’re unsure of how to accomplish this or you’re not working within a CMS, reach out to a developer or check out our SEO services to get you fixed up!
Changing and Removing Internal Links
Redirecting broken pages is a best practice for handling and mitigating a poor user experience. However, it should be noted that updating links or deleting them are vital options as well in the management of both internal and external broken links. Changing internal broken links to point to their new location helps preserve internal link equity and eliminates potential future issues if redirects are eventually removed. In some cases though, if the new location isn't a relevant match, deleting the link entirely is the best way to fix a broken internal link. Internal link relevance and anchor text relevance are vital to any sites internal linking structure. It's better to have no link at all than to link to a page that is no longer relevant to the topic or the anchor text being used.
Changing and Removing External Links
External links often fall into exclusively these categories as you don't have much control over other sites past asking nicely. Sometimes a site you linked to simply changed the URL without setting a redirect causing your link to break but the page more or less still exists. A bit of Google detective work can usually find these using 'site:' commands or other advanced operators like 'intitle:' or 'inurl:'.Sometimes though pages are just gone (see link rot) and if you’re unable to find any good replacement for a broken external link, then it's perfectly fine to simply remove the hyperlink and move on. Better to have no link than one that takes a user to a broken page off your site!
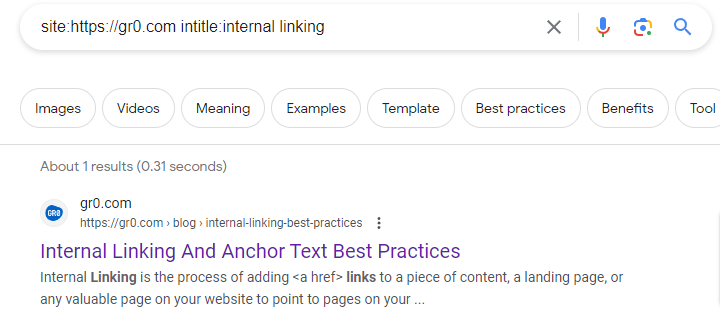
Checking Backlinks to Formerly Broken Pages
It's important to remember that your website's pages might have backlinks — links from other websites. If you've had broken links, chances are there may be external sites linking to these non-existent pages.
Use a backlink checker tool, like those provided by Ahrefs or SEMRush, to find these external links. Reach out to the webmaster of the corresponding site, informing them of the change and providing the new URL. While this method may not always bear fruit, we always recommend giving it a try.
Ongoing Maintenance and Prevention
Your task isn't over now that your broken links have been identified and fixed — broken links can recur, so continuous monitoring and prevention are key to maintaining a healthy website.
Regular Monitoring for New Broken Links
Consistent checking helps ensure that you catch and fix any new broken links as soon as they appear. Set a routine, like monthly or quarterly, to check for broken links using the methods described above.
At GR0, we recommend monthly checks for sites under 5,000 pages and Quarterly or twice yearly checks for bigger sites. Some of the tools we’ve suggested allow for automated crawl scheduling which can really help keep your website in good shape.
Maintain A Functional 404 Landing Page
It can be difficult to find every instance and plan for every occurrence where a broken page or link might exist. One of the best ways to mitigate any damage to your user’s experience on your site is with a 404 landing page that can inform, give options, and possibly even mildly entertain the user who finds a broken page.
In ecommerce, 404 landing pages can help direct customers to similar products when landing on an item that’s become broken due to being out of stock. In general, a good 404 landing page should at least give the user an option to go back to your homepage. Giving additional options to go to other key sections or search your site can also help users get back on the right track and keep them from leaving your site entirely.
One of our favorite clients, Litter-Robot, shows one great example of a 404 landing page that hits all the marks.

The versatile and effective 404 landing page for Litter-Robot
Link Checks During Website Updates
Website updates, including redesigns and migrations, often result in broken links. During any major site update, ensure to include a comprehensive link check in your process.
What Are Some Best Practices for Preventing Broken Links?
While it's important to monitor and fix broken links, it's equally beneficial to prevent them in the first place.
By following these best practices, you can significantly reduce the occurrence of broken links:
• Consistent URL Structure: Maintain a consistent URL structure across your website. This reduces the chances of creating incorrect internal links.
• Double-Check Before Publishing: Ensure to check all links, internal and external, before publishing any new content. One tiny mistake in a URL will cause a broken link.
• Use Reliable External Links: Linking to reliable external sources reduces the risk of those links breaking. Reputable websites are more likely to maintain their URLs or implement proper redirects if they do change.
• Check After Modifications: After modifying any web pages, such as during a site redesign, content update, or site migration, always check for broken links.
• Educate Your Team: If you have a team managing your website, ensure they are aware of the implications of broken links or pages and the importance of checking and fixing them.
By implementing these preventative measures and combining them with regular checks using the Google Search Console, manual checks, and website crawling tools, you can effectively manage and minimize the impact of broken links on your site's SEO and user experience.
Keep Your Website Linked
Finding and fixing broken links on your website is essential to maintaining a healthy and user-friendly website. Regular checks and timely fixes ensure a smooth user experience, thereby retaining user trust and boosting your site's SEO rankings.
Website maintenance is an ongoing process, not a one-time task. Keeping an eye out for broken links should be a part of your regular site audit routine. With the step-by-step guide outlined in this article, you should be well-equipped to manage broken links and, by extension, your website's overall performance.
Are you a site owner that wants your website checked by professionals? Send a message to GR0 requesting a custom quote today. If you’re an SEO and think you’d like to join our team, check out our digital marketing careers page and see if we’re hiring!
Sources:
HTTP Status Codes, Network and DNS Errors, and Google Search | Google
What the ephemerality of the Web means for your hyperlinks | Columbia Journalism Review
Table of Contents
In the highly competitive digital world, the success of your website hinges on numerous factors, one of them being the functionality of your links.
Broken links are a common, yet often overlooked, technical SEO issue that can significantly impact your site's quality, rankings, and overall user experience.
This article will serve as a comprehensive, step-by-step guide on how we at GR0 find and fix broken links on our client’s websites. We hope this guide will help demystify this facet of technical SEO and help you improve both your site's performance and your user's experience.
What Are Broken Links?
Broken links, also known as dead links, are links that lead to pages that do not exist. When a user or search engine bot tries to follow a broken link, they will usually encounter a “404 Error Page.” This error is among several HTTP status codes in the 400 or 4xx range, indicating broken or missing content and by far the most common.
The causes of broken links are diverse. They can occur when linked content is moved or deleted, causing what is known as link rot. A study by Harvard Law School of over 2 million hyperlinks showed that as time goes on, link rot on the web increases exponentially, with links from 10 years ago becoming broken at a 43% rate!

Source: https://www.cjr.org/analysis/linkrot-content-drift-new-york-times.php
Changes to the site's URL structure during a site migration, misspelled URLs, or page and content deletions can also cause broken links.
Why Is It Important To Fix Broken Links?
Broken links, be they internal links that lead to other pages on your site or external links directing to other websites, are detrimental in many ways.
Firstly, they disrupt the user experience. Clicking on a link only to be met with an error page is frustrating for users and may discourage them from further exploring your site. Any time a user doesn't get what they thought they would when they click a link on your site it encourages them to leave.
From an SEO perspective, broken links are harmful because search engines, like Google, consider them while determining the quality of your site. When a search engine's crawler, also known as a spider, encounters a large amount of broken links, it can signify poor maintenance. If too many of these are present it can lead to reduced crawling and potentially Google seeing your site as “low-quality.”
In the realm of digital marketing, trust is a valuable currency. Frequent encounters with broken links can erode your audience's trust, negatively affecting your brand reputation. While fixing broken links is often the most effective way to preserve your site’s quality, having a functional and attractive 404 landing page is an absolute must for preserving brand image and user experience. A 404 landing page can greet users and help them get back to useful content even if you’re unaware a broken link exists!
How To Check for Broken Internal Links
Knowing how to find broken pages and links is an all-important first step in beginning to fix the quality of your website. There are a handful of tools and methods SEOs use. We’ll cover below the ones we at GR0 use, and a few alternatives we think might be useful.
1. Use a Web Crawler
No SEO’s tool kit is complete without a proper web crawler. Website crawling tools or SEO spiders are designed to mimic how search engines crawl websites, thereby helping to uncover all sorts of SEO issues, including broken links. Using a web crawling tool is our first step in discovering where broken pages exist on sites as well as where those broken pages are linked to.
Selecting a Crawling Tool
There is no shortage of web crawlers available, both in paid and free versions. Some popular ones are Screaming Frog SEO Spider, SiteBulb, Botify, Jet Octopus, as well as the audit tools within larger tool suites like Ahrefs and SEMRush.
All these tools have their unique features and advantages, but they all perform the essential function of detecting broken links effectively. Here at GR0, we’re partial to Screaming Frog due to its versatility and ability to handle small, medium, and large sites fairly well. The free version even lets you crawl up to 500 pages which is great for small sites and those new to SEO!
Configuring Crawling Settings
After selecting your preferred tool, you'll need to configure it to suit your requirements. You can set up the crawler to scan all the pages or specific sections of your site. This is great if you have a larger site and you only want to focus on a particular portion. It must be noted, however, that to get the clearest picture of all the broken links across your site, crawling the entire site is the only way to go.
It's a good practice to ensure your SEO spider is set to follow both internal and external links though the fixes for these will be very different, If your site is heavily coded in JavaScript, you may need to make sure that rendering is turned on so it can find any links that only appear after a page is rendered.
We also suggest making sure your XML Sitemap is part of the crawl, as it functions as your list of all your pages you want search engines to see.

Analyzing Crawl Results for Broken Links
Once the crawl is complete, the tool will provide you with a report detailing all the information about your site's health, including broken pages. You can usually find these under “Response Codes” or “HTTP Status” and look for 4xx errors, these can also be sorted by internal or external pages. In Screaming Frog, you need to select a broken page and then select the “inlinks” tab at the bottom to see all the places your site links to this broken page.

These tools often allow you to export data into Google Sheets, CSV, or Excel formats, we recommend exporting the inlinks to your broken pages so you sort and prioritize your issues. Obviously, the more links leading to a broken page, the bigger the issue, so use this to help maximize your efforts.
Something we always suggest, too, is manually checking your pages to be certain they’re actually broken and the links still exist. While things like AI and automated tools are great and can save tons of time, they’re not perfect.
2. Manual Checks
While this method isn’t suitable for sites with more than a handful of pages, we always encourage checking the status and links on a representative sample or key pages manually. Prioritize your most important pages, like the home page, social media links, and blog posts. Simply visit the page containing broken links and click them.
Using the data from your crawling tool, you can even narrow down the anchor text and surrounding content to make sure you’re following the problem links.
If you do encounter a link that says it's broken but actually works, it’s alright to move along and skip that. User experience is the key reason for fixing broken links, so if that is satisfactory, you’re usually in good shape. If large amounts of your broken links end up working, it might be time to ask for help (like reaching out to the professionals here at GR0), as you may have a deeper issue causing your site to appear broken.
Identifying Broken Links With Browser Extensions
You can also use browser extensions to check links. Extensions like the Ahrefs Toolbar (our favorite) and “Check My Links” for Chrome are free tools that scan web pages for broken links, highlighting them for easy identification. WordPress users can benefit from plugins like “Broken Link Checker,” which monitor and detect broken links.
This manual process can be tiresome and time-consuming, especially for larger websites. This is why we recommend starting with tools like website crawlers, like Screaming Frog, SEO browser extensions, and Google Search Console can be quite useful.
3. Using Google Search Console
As one of the most effective and free tools at your disposal, Google Search Console (GSC) should be among the first ports of call in your SEO journey. GSC is a site owner and SEO’s clearest look into how our sites perform and how Google sees and crawls a website. It helps monitor, troubleshoot, and improve your site's presence in Google Search results, broken links included.
How To Use Google Search Console
To begin using Google Search Console, you'll need to add and verify your ownership. Once your site is verified, navigate to the “Pages” report in the “Indexing” section. This report shows you any issues that Google's crawlers have found when indexing your website, including your broken pages.
The biggest section of this report is the “Why Pages Aren’t Indexed” section which is a massively useful tool for all aspects of your website's health.

Here, you'll find a list of URLs that Google couldn't find on your site, which usually means they're broken. Since Google crawls the entire web more than anyone, it can turn up broken pages an SEO crawler may not find.
Monitoring and Resolving Broken Links
Google Search Console is a great additional tool to check for broken pages you might have missed, as well as to see what Google thinks about the broken pages on your site. You can even use Google’s URL inspector on these pages to sometimes see the exact page Google found a broken link to your pages on. While it won’t give you every place you can find a potential broken link, it can help start your journey.
Keep in mind, Google Search Console updates its data every few days. Check the “last crawled” date next to your results to know when Google last identified this URL as broken. Google even gives you a button to validate your fixes once you’re done. Don't panic if the broken link still appears after you've fixed it and started validation. This process can take weeks or even months, depending on the size of your site.
How To Fix Broken Internal and External Links
Once you have identified the broken pages, the next step is implementing fixes. In this context, There are 3 key methods to fix broken internal links: removing the broken link, changing the broken link to a working URL and setting redirects on the broken pages.
Creating 301 Redirects for Internal Links
The 301 redirect is the most commonly used method to fix broken links. When you apply a 301 redirect to a broken URL, you're telling search engines that the page has permanently moved to a new location. According to Google both permanent (301) and temporary (302) redirects help to preserve rankings and pass link equity associated with the old URL. Google recommends you keep 301 redirects in place for at least a year to ensure all equity passes from the old page to the new. Evidence also suggests that over time Google will treat a temporary 302 redirect like its permanent so if you forget or see a 302 instead of a 301 it isn't a cause for great concern. Google's John Mueller lays out on twitter how this might happen:

If you’re working within a CMS like WordPress, Wix, or Shopify, they will have methods within their system and rules that will allow you to designate what pages need to receive these redirects. If you’re unsure of how to accomplish this or you’re not working within a CMS, reach out to a developer or check out our SEO services to get you fixed up!
Changing and Removing Internal Links
Redirecting broken pages is a best practice for handling and mitigating a poor user experience. However, it should be noted that updating links or deleting them are vital options as well in the management of both internal and external broken links. Changing internal broken links to point to their new location helps preserve internal link equity and eliminates potential future issues if redirects are eventually removed. In some cases though, if the new location isn't a relevant match, deleting the link entirely is the best way to fix a broken internal link. Internal link relevance and anchor text relevance are vital to any sites internal linking structure. It's better to have no link at all than to link to a page that is no longer relevant to the topic or the anchor text being used.
Changing and Removing External Links
External links often fall into exclusively these categories as you don't have much control over other sites past asking nicely. Sometimes a site you linked to simply changed the URL without setting a redirect causing your link to break but the page more or less still exists. A bit of Google detective work can usually find these using 'site:' commands or other advanced operators like 'intitle:' or 'inurl:'.Sometimes though pages are just gone (see link rot) and if you’re unable to find any good replacement for a broken external link, then it's perfectly fine to simply remove the hyperlink and move on. Better to have no link than one that takes a user to a broken page off your site!

Checking Backlinks to Formerly Broken Pages
It's important to remember that your website's pages might have backlinks — links from other websites. If you've had broken links, chances are there may be external sites linking to these non-existent pages.
Use a backlink checker tool, like those provided by Ahrefs or SEMRush, to find these external links. Reach out to the webmaster of the corresponding site, informing them of the change and providing the new URL. While this method may not always bear fruit, we always recommend giving it a try.
Ongoing Maintenance and Prevention
Your task isn't over now that your broken links have been identified and fixed — broken links can recur, so continuous monitoring and prevention are key to maintaining a healthy website.
Regular Monitoring for New Broken Links
Consistent checking helps ensure that you catch and fix any new broken links as soon as they appear. Set a routine, like monthly or quarterly, to check for broken links using the methods described above.
At GR0, we recommend monthly checks for sites under 5,000 pages and Quarterly or twice yearly checks for bigger sites. Some of the tools we’ve suggested allow for automated crawl scheduling which can really help keep your website in good shape.
Maintain A Functional 404 Landing Page
It can be difficult to find every instance and plan for every occurrence where a broken page or link might exist. One of the best ways to mitigate any damage to your user’s experience on your site is with a 404 landing page that can inform, give options, and possibly even mildly entertain the user who finds a broken page.
In ecommerce, 404 landing pages can help direct customers to similar products when landing on an item that’s become broken due to being out of stock. In general, a good 404 landing page should at least give the user an option to go back to your homepage. Giving additional options to go to other key sections or search your site can also help users get back on the right track and keep them from leaving your site entirely.
One of our favorite clients, Litter-Robot, shows one great example of a 404 landing page that hits all the marks.

The versatile and effective 404 landing page for Litter-Robot
Link Checks During Website Updates
Website updates, including redesigns and migrations, often result in broken links. During any major site update, ensure to include a comprehensive link check in your process.
What Are Some Best Practices for Preventing Broken Links?
While it's important to monitor and fix broken links, it's equally beneficial to prevent them in the first place.
By following these best practices, you can significantly reduce the occurrence of broken links:
• Consistent URL Structure: Maintain a consistent URL structure across your website. This reduces the chances of creating incorrect internal links.
• Double-Check Before Publishing: Ensure to check all links, internal and external, before publishing any new content. One tiny mistake in a URL will cause a broken link.
• Use Reliable External Links: Linking to reliable external sources reduces the risk of those links breaking. Reputable websites are more likely to maintain their URLs or implement proper redirects if they do change.
• Check After Modifications: After modifying any web pages, such as during a site redesign, content update, or site migration, always check for broken links.
• Educate Your Team: If you have a team managing your website, ensure they are aware of the implications of broken links or pages and the importance of checking and fixing them.
By implementing these preventative measures and combining them with regular checks using the Google Search Console, manual checks, and website crawling tools, you can effectively manage and minimize the impact of broken links on your site's SEO and user experience.
Keep Your Website Linked
Finding and fixing broken links on your website is essential to maintaining a healthy and user-friendly website. Regular checks and timely fixes ensure a smooth user experience, thereby retaining user trust and boosting your site's SEO rankings.
Website maintenance is an ongoing process, not a one-time task. Keeping an eye out for broken links should be a part of your regular site audit routine. With the step-by-step guide outlined in this article, you should be well-equipped to manage broken links and, by extension, your website's overall performance.
Are you a site owner that wants your website checked by professionals? Send a message to GR0 requesting a custom quote today. If you’re an SEO and think you’d like to join our team, check out our digital marketing careers page and see if we’re hiring!
Sources:
HTTP Status Codes, Network and DNS Errors, and Google Search | Google
What the ephemerality of the Web means for your hyperlinks | Columbia Journalism Review
Let's get started
We’re so excited to bring your story to life. What can we do for you?



